《剑桥学霸高能英语学习法》
第 20节课后资料 《时态详解》
讲师:杨孟衡
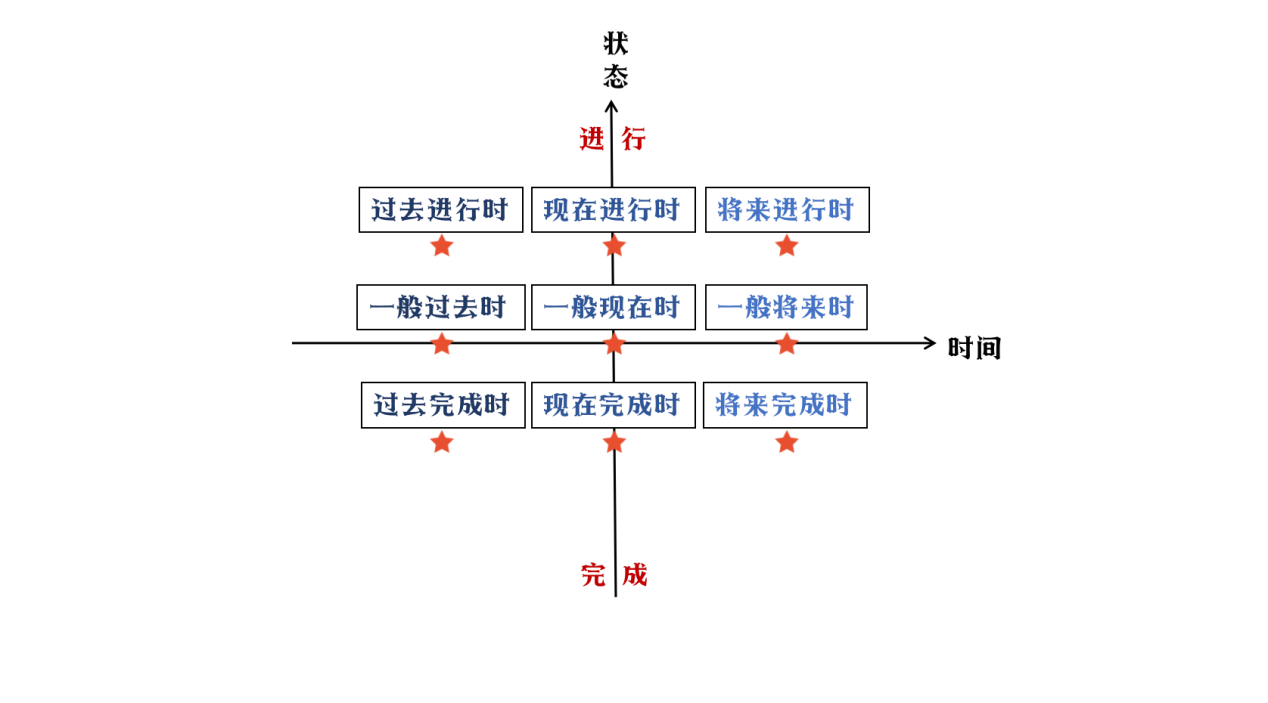
常用的九种时态
一、 一般现在时
1. 表客观真理、科学事实、格言或不受时间限制的客观存在
Knowledge is power.
In summer, days are longer than nights and in winter it is the opposite.
2. 表现在的习惯动作(通常用动作动词,与频度副词连用)
What does your brother do?
He always goes to work late, which makes the boss anger and disappointed.
3. 表示现在正在发生的动作或存在的状态
Here comes the bus.
一般现在时用在以there或here开头的句子中,表示目前的短暂动作。如上述例句中,说话人看到bus正在驶来,然后说了这句话,即表示正在发生的动作,所以当表达车正在驶来时,固定说成“Here comes the bus.”。但这个结构不能用现在进行时,不能说“Here is coming the bus.”(×)只能说成“The bus is coming.”但此时的进行时表示将来动作,所以句意为“公共汽车很快就要来了。”
How hard it snows!
4. 表示瞬间动作(通常用于新闻报导、现场直播)
Li passes the ball to Wu. Wu heads it to Chen. Chen shoots, and the goalkeeper leaps for it. Oh, it’s a goal.
5. 表示将来时间
A. 根据时间表或规定预计要发生的事
What time does the train leave?
Tomorrow is Saturday.
I retire next year.
B. I hope… I bet..., see to...等后的宾语从句中通常用一般现在时表将来意义,但有时也可直接用将来时态。
I hope that you like(will like).
I bet it rains(will rain) tomorrow.
See (to it) that children don’t catch cold.
I’ll see that nobody disturbs(will disturb) you.
(注:see to it 后的that从句通常用一般现在时表将来,直接用将来的情形较少见。)
C. 在make sure, make certain, take care, be careful, mind, watch等后的that从句中
Take care that it does not occur again.
Make sure you come back soon.
Mind you read the examination questions carefully before you begin to answer them.
D. …if/when/while/as soon as…
I’ll tell her when she comes back. (在条件或时间状语从句中,如果主句是将来时,从句可用现在时态表示将来的时态)
二、 一般过去时
1. 过去所发生的动作、状态,与现在没有联系
He was a teacher all his life. (人已经死了)
2. 表示过去习惯的动作: e.g. used to do sth., would do sth.
The boy sold newspaper for a living.
3.在特定句型中,表现在时间和将来时间
A. 日常用语、客气的语气
Did you want to see me?
I wondered if…
B. It’s (high) time that… (很客气的一种建议)
I wish I were young as you.
I’d rather you went now.
If only…
…as if...
(虚拟) He looks as if he were ill. (假病)
(陈述) He looks as if he is ill. (真的病了)
I feel as if my head were on fire.
Suppose we spent next Sunday in the country.
三、 一般将来时
(一) 表示一般将来时的动词形式及用法
1. 用情态助动词shall/will + 动词原形表示
A. 表示“预见”——时间
They will go to a concert this evening.
B. 表示“意图(愿)”,没有将来的意思,有个人感情成分
No, I won’t lend it to you.
2.用“be going to do sth.”表示
A. 表示“预见”——有迹象表明,将来某个时刻,将发生某事
Be careful! The pile of boxes is going to fall.
B. 表示“意图”——经过考虑的,打算在近期做的
I’m going to Beijing.
How long are you going to stay here?
3.用“be doing”表示——按即或安排将发生的动作
The plane is taking off at twelve.
特点:a. 用时间状语以区别于现在进行时
b. 意思靠上下文来理解:Hurry up! The train is starting.
4.用“be to do sth.”
A. 表示按计划安排
We are to learn Chapter Six next week.
B. 报纸或电视台宣布官方正规的消息
Premier Li is to visit Japan next week.
The highway is to open to traffic next Sunday.
C. 表命令、禁止,没有将来的意思
You are to stay here!
No one is to leave the classroom without my permission.
6. 用一般现在时的动词形式表示将来时间
一般现在时表示将来主要指按计划安排将要发生的事,这种安排不可更改或不能随意变动。
The sports meeting takes place on October 18.
(二)各种表示一般将来时的动词形式的用法比较
1.Will/shall + 动词原形和be going to结构的比较
A. 都表示意图,可互换
B.预先经过考虑的,用“be going to”
She has bought some cloth. She is going to make herself a dress.
C.事先没有考虑的,用“will”表意愿
I will go. I will help you.
2.be + V.-ing和be going to结构的比较
A.表将来,现在已觉得做时,两者可互换
B.be + V.-ing: 肯定,不容改变的安排,比较正式
be going to: 有迹象表面将发生某事
3.will/shall+动词原形和将来时表示将来时间的比较
If you will (will表意愿,不能略写) kindly wait for a moment, I’ll ask the manager to speak to you.
四、 现在进行时
(一) 用法
1. 表示说话时正在进行的动作
Now watch carefully and see what is happening in the experiment.
2. 表示现阶段正在进行的动作(讲话时不一定在做)(暂时性)
George is working on a new book about stories in school.
3. 表计划安排中近期将发生的动作(有时间状语)
I am taking my daughter to the Central Park this Saturday.
4. 表示刚过去的动作,动词为某些表示说话的词:talk, tell, say等
Believe it or not, I am telling the truth.
5. 表示婉转的语气:I’m hoping/wanting/wondering if… (在口语中)
6. 与always等频度副词连用,表示感情色彩的现阶段发生的动作
He’s always finding our faults. (表厌烦)
He’s always borrowing money from me and forgetting to pay it back.
(二) 一般现在时与现在进行时的用法比较
1. 相对而言,一般现在时表示经常性动作,现在进行时表示暂时性动作
I live in Guangzhou. (长期)
She’s living in Guangzhou. (读书期间,暂时)
2. 在报道中,一般现在时表示短暂动作,现在进行时表示持续动作
He shoots, and it’s a goal. The crowd is cheering and the other players are running to him to…
The bus stops. (一下子停下)
The bus is stopping. (慢慢停下)
3. 一般现在时用来叙述事实,现在进行时含有某种感情色彩(不加频率副词时有赞扬的语气)
You are doing fine in school.
五、 过去进行时
1. 表示过去某一时间正在进行的动作
When he called me, I was having dinner.
I was washing the dishes while Mother was clearing up the table.
2. 表示过去某段时间的暂时性动作
At that time I was teaching in Beijing.
3. 表示按计划安排过去某时将发生的动作(有时间状语)
He was leaving a few days later. (表示过去将来时)
4. 表示婉转口气:want, hope, wonder
I was wondering if…
5.在某些结构中做想象的用法,表示对现在或将来的设想(虚拟语气)
I wish he weren’t speaking so loudly. (与现在事实相反)
If they were leaving tonight, I’d like to go with them. (与将来事实相反)
6.与频度状语连用,表示感情色彩
He was always changing his mind.
7. 作为铺叙故事情节的背景
A man was ferrying across the river when his sword fell into the river.
六、 将来进行时
"shall/will + be +现在分词"
将来进行时表示要在将来某一时间开始,并继续下去的动作。一般用延续性动词表示。在英语时态中,“时“指动作发生的时间,”态“指动作的样子和状态。 常用来表示礼貌的询问、请求或期待等。
Please don't call me between 8:00 and 10:00 tomorrow. I'll be having my classes then.
Will you be using your bicycle this evening?
七、 现在完成时
have/has + 过去分词
1. 过去某时发生的动作,其结果和影响现在依然存在
I’ve traveled by plane. (有此经历,不确切的过去时间)
Do you understand what I have said? (动作的先后)
与时间状语连用的情况:
A. 可以与不确切的过去时间状语连用:already, yet, before, recently, lately...
He has already phoned me about the theft.
B. 可以与频度状语连用:sometimes, ever, never, once, often…
I have only been to the Great Wall once.
C. 可以与包括现在时间在内的时间状语连用:this month/morning…,但暗示着另外一个问题
The rain has stopped now (=at last).
2.(现在)未完成用法:过去发生的动作持续到现在,也许还会持续下去
A.与since引导的时间状语连用:since + 名词词组/从句
I’ve been here since last July.
She has taught us since I came to this school.
B.由for引导的时间状语,表一段时间
I haven’t seen her for two years.
C.可以和其他表示包括现在时间在内的一段时间的时间状语连用:until now, in the past few years, all morning…
Great changes in every fields have taken place in the past few years.
八、 过去完成时
had + 过去分词
1. 表示一个动作或状态在过去某一时间或某一动作之前已经发生(过去的过去)
He flew home, but his father had died.
2. 表示一个动作或状态在过去某一时间之前已经开始,一直延续到这一过去时间还没结束(用段时间的时间状语)
By six o’clock, they had worked for 24 hours.
She said she had made great progress since she came here.
3. 想象性用法(虚拟语气)
I wish I had gone with you yesterday.
4.表示过去未曾实现的希望、愿望、打算:hope, want, think, expect, intend, suppose…
We had hoped you would (be able to) go with us.
We had wanted to help but couldn’t get there in time.
九、 将来完成时
shall(第一人称)will(第二、三人称)+have+过去分词(done)
将来完成时是用在表示在将来某一时间以前已经完成或一直持续的动作。常用“by+表示将来时间的短语或句子”或“when/after 等+表示将来动作的句子”作时间状语。
We shall have finished the project by the end of this year.
They will have moved to the new house when it has been painted.

